
Overdose symptoms seroquel can be alarming and dangerous. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of an overdose, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
Seroquel is a medication often prescribed for the treatment of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and depression. While it can be highly effective when used as prescribed, taking too much of the medication can lead to serious consequences.
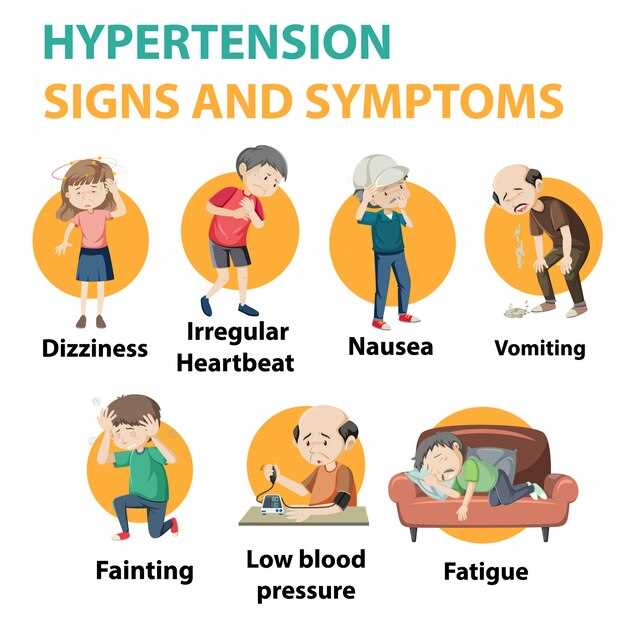
Some common overdose symptoms of seroquel include:
- Extreme drowsiness
- Agitation or restlessness
- Fast heart rate
- Low blood pressure
- Fainting
- Confusion
- Seizures
If you or someone you know is experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to call emergency services or go to the nearest emergency room immediately. Delaying medical care can have serious consequences.
Remember, your health and well-being are important. If you suspect an overdose or have concerns about your medication, consult with a healthcare professional as soon as possible. They can provide proper guidance and support to ensure your safety and recovery.
Overview
The importance of recognizing overdose symptoms is crucial when it comes to medications like Seroquel. Seroquel, also known as quetiapine, is an antipsychotic medication used to treat conditions such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. While Seroquel can be an effective treatment option, it is important to be aware of the potential risks and side effects, including the possibility of overdose.
Understanding Seroquel
Seroquel works by targeting certain receptors in the brain, specifically dopamine receptors, to help regulate the balance of chemicals in the brain. It is believed to help reduce the symptoms of conditions such as hallucinations, delusions, and mood swings.
Importance of Recognizing Overdose Symptoms
Recognizing overdose symptoms is crucial because it can help prompt immediate medical attention, which is necessary in case of an overdose. An overdose on Seroquel can be life-threatening, and early intervention can greatly increase the chances of a successful recovery.
Some common signs and symptoms of Seroquel overdose include:
- Extreme drowsiness or sedation
- Confusion
- Rapid heartbeat
- Low blood pressure
- Fainting
- Seizures
- Uncontrollable shaking or tremors
- Difficulty breathing
- Blurred vision
- Unusual muscle contractions
If you or someone you know is experiencing any of these symptoms after taking Seroquel, it is important to seek immediate medical attention. Remember, recognizing overdose symptoms and taking prompt action can save lives.
Importance of recognizing overdose symptoms
Recognizing overdose symptoms is of utmost importance when taking Seroquel. An overdose occurs when an individual takes more than the prescribed dose of Seroquel, which can lead to serious health complications. By understanding the signs and symptoms of an overdose, individuals can take immediate action to seek medical help and prevent any potential harm.
Why is it important?
Identifying overdose symptoms is crucial because Seroquel, also known as quetiapine, is an antipsychotic medication that affects the chemicals in the brain. Taking an excessive amount of Seroquel can result in various physical and cognitive symptoms that require prompt medical attention.
What happens during an overdose?
During a Seroquel overdose, the individual may experience an amplified effect of the drug, causing severe sedation, confusion, and an increased heart rate. Some common symptoms of a Seroquel overdose include:
| Physical Symptoms | Cognitive Symptoms |
| – Drowsiness | – Confusion |
| – Rapid heartbeat | – Delirium |
| – Low blood pressure | – Difficulty speaking |
| – Fainting | – Memory problems |
| – Seizures | – Hallucinations |
If you or someone you know shows any of these symptoms while taking Seroquel, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. An overdose of Seroquel can be life-threatening, and prompt medical intervention is vital to ensure the individual’s safety and well-being.
Understanding Seroquel
Seroquel is a prescription medication that belongs to a class of drugs called atypical antipsychotics. It is primarily used to treat conditions such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Seroquel works by affecting the chemicals in the brain that are responsible for mood and behavior.
Unlike traditional antipsychotic medications, Seroquel has a lower risk of causing movement disorders. It is believed to work by blocking the receptors for certain neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and serotonin, in the brain.
Seroquel is available in tablet form and is usually taken once or twice a day. The dosage may vary depending on the condition being treated and the individual’s response to the medication.
It is important to note that Seroquel should only be taken under the supervision of a healthcare professional. It is not recommended for use in children or adolescents unless specifically prescribed by a doctor.
Prior to starting treatment with Seroquel, it is important to discuss any existing medical conditions or medications with your doctor. Seroquel may interact with certain medications or conditions, and your doctor will need to determine if it is safe for you to take.
In conclusion, understanding Seroquel is crucial for individuals who are prescribed this medication. By understanding how Seroquel works and its potential benefits and risks, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment plan.
What is Seroquel
Seroquel is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs called atypical antipsychotics. It is used to treat certain mental/mood conditions such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and depression. Seroquel works by helping to restore the balance of certain natural substances in the brain.
Seroquel is often prescribed to:
- Treat symptoms of schizophrenia such as hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking.
- Manage episodes of mania or depression in patients with bipolar disorder.
- Relieve symptoms of depression when used as an adjunct treatment.
Seroquel is available in the form of tablets and extended-release tablets. The dosage and duration of treatment will depend on the specific condition being treated and the individual patient’s response to the medication. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and instructions provided by a healthcare professional.
Note: Seroquel should not be used for dementia-related psychosis as it may increase the risk of death in elderly patients with this condition.
Overall, Seroquel is an important medication that has been shown to be effective in treating certain mental/mood conditions. If you have been prescribed Seroquel, it is important to take it as directed and communicate any concerns or side effects to your healthcare provider.
How Seroquel works
Seroquel is classified as an atypical antipsychotic medication, and its active ingredient is quetiapine fumarate. It works by affecting the activity of certain chemicals in the brain, including dopamine and serotonin.
Dopamine and serotonin are neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that transmit signals between nerve cells in the brain. They play a role in regulating mood, sleep, and other cognitive functions.
Seroquel blocks the receptors in the brain that dopamine and serotonin normally bind to. By blocking these receptors, Seroquel helps to balance the levels of these neurotransmitters in the brain, which can reduce symptoms of certain mental disorders.
It is believed that Seroquel’s effects on dopamine and serotonin receptors help to regulate the activity in certain areas of the brain, such as the prefrontal cortex and limbic system, which are involved in mood regulation. This can help to alleviate symptoms associated with conditions like schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
Additionally, Seroquel has effects on other receptors in the brain, including histamine receptors and adrenergic receptors. These additional effects may contribute to its sedative and calming effects.
Overall, the exact mechanism of action of Seroquel is not fully understood, but it is thought to involve a combination of effects on several neurotransmitters and receptors in the brain.
Signs and Symptoms of Overdose
An overdose of Seroquel, a medication used to treat certain mental and mood disorders, can have serious consequences. It is essential to recognize the signs and symptoms of an overdose to ensure prompt medical attention and intervention.
Physical symptoms:
Physical symptoms of a Seroquel overdose may include extreme drowsiness, rapid heart rate, low blood pressure, difficulty breathing, and seizures. These symptoms can be life-threatening and should be treated as a medical emergency.
Cognitive symptoms:
In addition to physical symptoms, an overdose of Seroquel can also affect a person’s cognitive abilities. Some common cognitive symptoms of overdose include confusion, disorientation, delirium, and hallucinations. These mental changes can be distressing and may require immediate medical intervention.
If you suspect someone may be experiencing a Seroquel overdose, it is crucial to seek medical help immediately. Prompt treatment can help prevent further complications and ensure the individual receives the necessary care.
Note: This information is not exhaustive, and it is essential to consult a healthcare professional or read the medication’s packaging for a complete list of signs and symptoms of an overdose.
Physical symptoms
An overdose of Seroquel can lead to various physical symptoms. These symptoms may vary depending on the individual and the amount of the drug consumed. Some common physical symptoms of a Seroquel overdose include:
| Physical Symptoms |
|---|
| Extreme drowsiness or sedation |
| Slurred speech |
| Unsteady gait or lack of coordination |
| Rapid heartbeat |
| Dilated pupils |
| Fluctuating blood pressure |
| Involuntary muscle movements |
| Impaired judgment and decision-making |
Extreme drowsiness or sedation
One of the most noticeable physical symptoms of a Seroquel overdose is extreme drowsiness or sedation. A person may struggle to stay awake and may appear excessively sleepy or lethargic.
Slurred speech
Another physical symptom of a Seroquel overdose is slurred speech. The person’s speech may become difficult to understand, with words sounding mumbled or garbled.
Unsteady gait or lack of coordination
A Seroquel overdose can also result in an unsteady gait or lack of coordination. The person may have difficulty walking or may stumble and fall easily.
Rapid heartbeat
Rapid heartbeat is a common physical symptom of a Seroquel overdose. The person’s heart rate may increase significantly, leading to feelings of palpitations or a pounding heart.
Dilated pupils
Dilated pupils are a physical sign that someone has taken too much Seroquel. The person’s pupils may appear larger than usual and may not constrict properly in response to light.
Fluctuating blood pressure
Fluctuating blood pressure is another physical symptom that can occur in cases of Seroquel overdose. The person’s blood pressure may increase or decrease rapidly, resulting in feelings of lightheadedness or dizziness.
Involuntary muscle movements
Involuntary muscle movements, such as tremors or jerking motions, can occur in cases of Seroquel overdose. These movements may be noticeable and uncontrollable.
Impaired judgment and decision-making
A Seroquel overdose can also lead to impaired judgment and decision-making abilities. The person may have difficulty thinking clearly and may make choices that are irrational or dangerous.
Cognitive symptoms
In addition to physical symptoms, an overdose of Seroquel can also cause various cognitive symptoms. These symptoms can have a significant impact on a person’s mental state and functioning. It is important to be aware of these cognitive symptoms so that they can be recognized and addressed promptly.
- Confusion: Experiencing confusion or disorientation is a common cognitive symptom of a Seroquel overdose. Individuals may struggle to think clearly or remember things accurately.
- Impaired judgment: Overdosing on Seroquel can also affect a person’s judgment and decision-making abilities. They may have difficulty making rational choices or exhibit impulsive behaviors.
- Memory problems: An overdose can lead to memory-related issues, including difficulties with both short-term and long-term memory. Individuals may have trouble recalling recent events or recalling information from the past.
- Slowed thinking: Seroquel overdose can also result in slowed cognitive processing. Thoughts may become sluggish and it may be challenging to process information or engage in complex mental tasks.
- Delirium: Severe cases of Seroquel overdose can lead to delirium, a state of severe confusion and disorientation. It may involve hallucinations, agitation, and extreme restlessness.
If you or someone you know is showing signs of a Seroquel overdose, including cognitive symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately. Prompt treatment can help prevent further complications and ensure the individual’s safety and well-being.
